TALL and TALL-3D: Thermal-hydraulics ADS Lead-bismuth Loop
The TALL test facility was designed to study thermal-hydraulics of heavy liquid metal (lead-bismuth eutectic) which is a potential candidate for both coolant and spallation target of accelerator-driven systems (ADS), as well as a coolant candidate for FBRs. The facility is scaled 1:1 in height with a volumetric scaling based on a single heat exchanger tube, comparing with an experimental ADS design. The present experiments on TALL are to support design and safety of ADS and lead-cooled fast reactor (LFR), concerned with EU projects for transmutation and Generation-IV reactors, respectively.
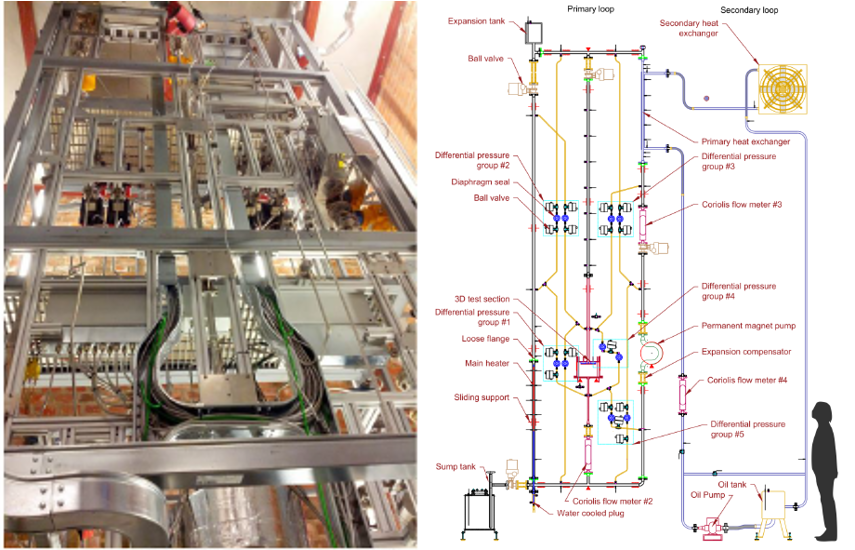
The facility is 6.8m tall and the placement of core tank (Item 2 in Fig.1b) and heat exchanger (Item 14 in Fig.1b) allows significant natural convection. The core tank has two designs for different studies. The first (Fig.1c) is made of made of a 316 stainless steel pipe with the outside diameter of 114 mm. It has the volume of around 3 liters, accommodating four immersion heaters (7 kW each). The core tank was scaled so that it can represent the reactor core of a conceptual ADS design corresponding to one tube of the heat exchanger, especially from the aspects of flow resistance and coolant inventory. The second (Fig.1d) is made of stainless steel tube with the inside diameter of 19 mm, in which a fuel rod simulator, the THERMOCOAX electric heater with a diameter of 8.2 mm and a heating length of 870 mm, is concentrically inserted. The power rating of the heater is 22 kW under the power supply of 85 volts and 265 amps. Investigation is also carried out for straight-tube and U-tube heat exchangers with counter-current flow arrangement. They are all made from a pair of 1-meter-long concentric ducts, with the LBE flowing in the inner tube of 10mm ID and the secondary coolant flowing in the annulus.
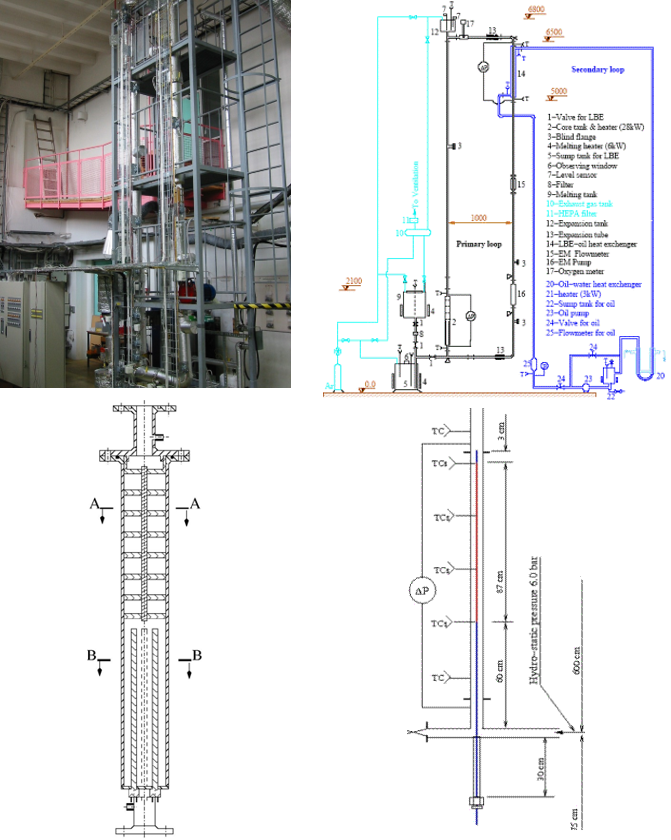
The working fluid of the primary side is liquid lead-bismuth eutectic (LBE), whereas the secondary side is filled with high-temperature organic coolant. Heat is generated in the core tank in the bottom of the left leg of the primary loop (the core leg), and transferred between the primary and secondary sides via a counter-current heat exchanger located in the top of the right leg of the primary loop (the HX leg). The heat is dissipated in an ultimate heat sink (via water pool or air radiator) in the secondary loop. An electromagnetic (EM) pump is installed to provide the driving head for the forced circulation mode of the facility, and EM and Coriolis flowmeters are employed to measure the flowrates.
To investigate the mixing phenomenon and possible thermal stratification in a pool-type design of lead-cooled reactor, a middle leg was added to the TALL test facility, which accommodates a test section simulating a cylindrical LBE pool with an inner height of 200 mm and inner diameter of 300 mm. The pool can be fully mixed (uniform temperature distribution) or thermally stratified. The test section was called as 3D test section, and accordingly the middle leg was called as 3D leg.